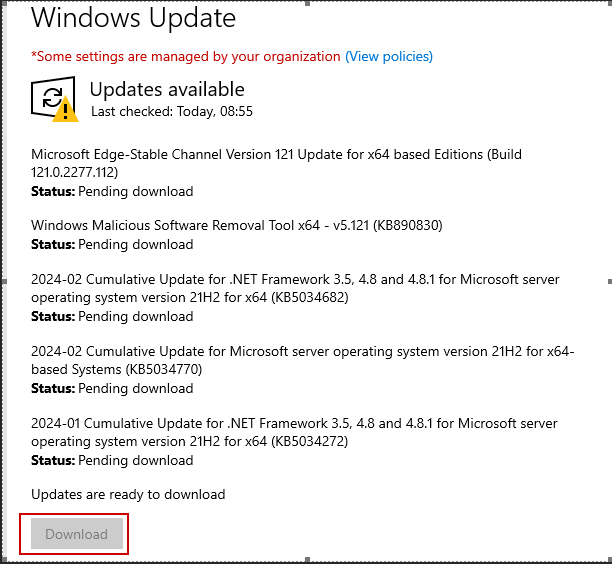
When a file is moved to a different folder on the same NTFS volume, its permissions don’t automatically update to match the destination folder’s settings. Instead, the file keeps its original permissions, which can lead to unexpected access issues if the destination has different security settings
To ensure files inherit the permissions of their new location when moved within the same NTFS volume, you can adjust the Windows Registry to change this behavior. Set the following registry key on the file server:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Explorer
MoveSecurityAttributes
REG_DWORD 0
EDIT:
This key does not work on newer Windows Server Operating Systems. It worked on Windows XP/Server 2003.
Reading time: 1 min